Design Thinking Overview
A human-centered approach to innovation
One of the most effective frameworks for innovation and problem-solving across industries. It combines creative and analytical approaches, emphasizing deep user understanding and iterative development to create meaningful solutions.
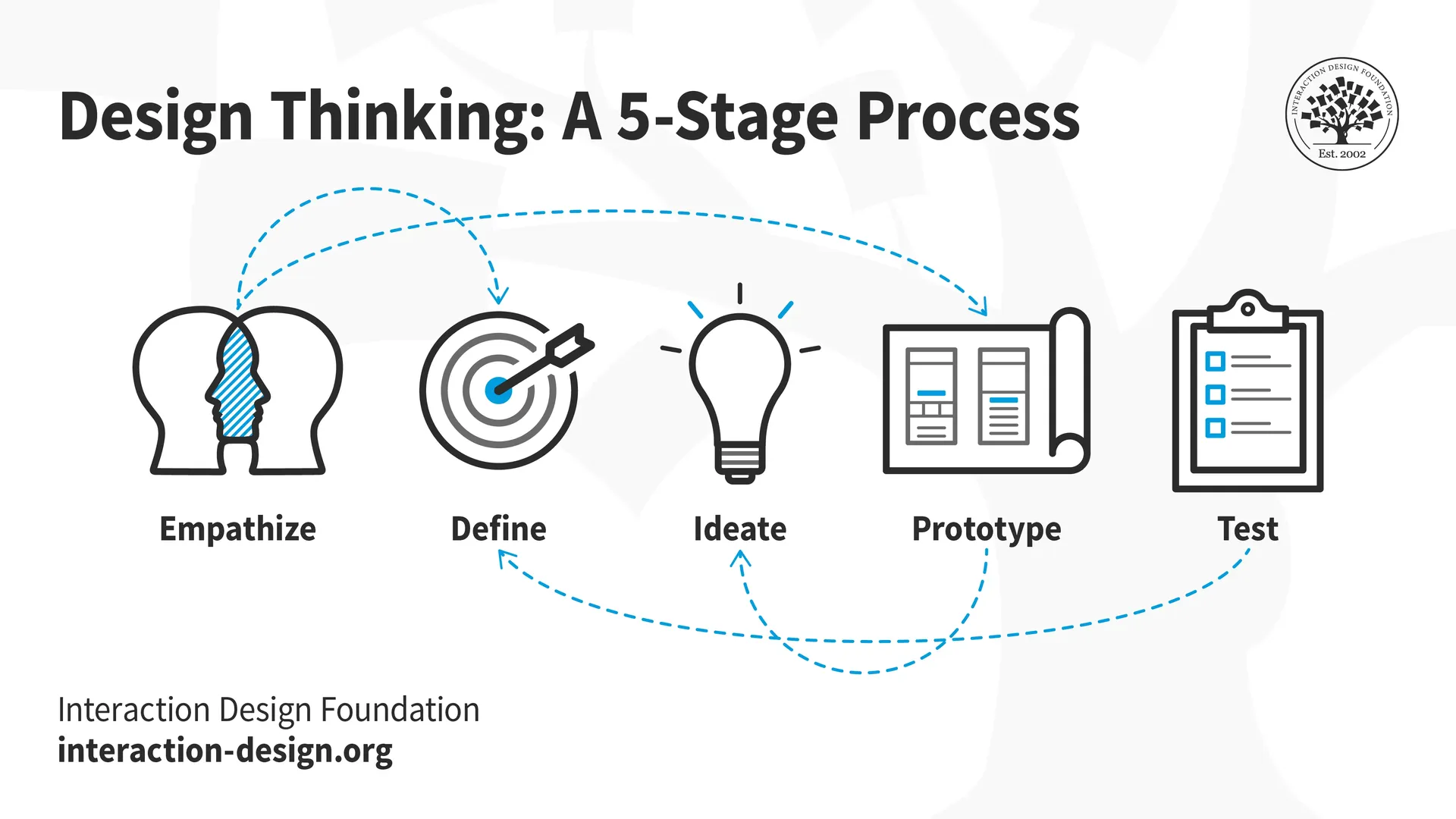
What Is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a methodology that places human needs at the center of the problem-solving process. It combines empathy, creativity, and rationality to meet user needs and drive innovation. This approach helps teams:
- Focus on user needs rather than assumptions
- Challenge traditional problem-solving methods
- Generate innovative solutions through iteration
- Test ideas early to reduce risk
- Build consensus through shared understanding
The Five Core Stages
1. Empathize
The foundation of human-centered design is understanding the people you’re designing for.
Key Activities:
- User interviews and observations
- Immersion in the user’s environment
- Journey mapping
- Gathering user stories
- Identifying pain points and gains
Outputs:
- User insights
- Behavior patterns
- Need statements
- Experience maps
2. Define
Transform research into clear problem statements that guide solution development.
Key Activities:
- Synthesizing research findings
- Identifying core problems
- Creating “How Might We” statements
- Prioritizing challenges
- Framing opportunities
Outputs:
- Problem statements
- Design criteria
- Project scope
- Success metrics
3. Ideate
Generate a wide range of creative solutions through collaborative ideation.
Key Activities:
- Brainstorming sessions
- Mind mapping
- Concept sketching
- Alternative worlds
- “Yes, and…” building
Outputs:
- Solution concepts
- Innovation opportunities
- New approaches
- Creative directions
4. Prototype
Create quick, low-fidelity representations of solutions to learn through making.
Key Activities:
- Rapid prototyping
- Paper modeling
- Digital mockups
- Role-playing
- Storyboarding
Outputs:
- Physical prototypes
- Digital prototypes
- Experience prototypes
- Service blueprints
5. Test
Gather user feedback through prototype testing to refine solutions.
Key Activities:
- User testing sessions
- Feedback collection
- Observation
- A/B testing
- Usability studies
Outputs:
- User feedback
- Improvement areas
- Validation points
- Next steps
Core Principles
1. Human-Centered
- Focus on user needs and experiences
- Build empathy through research
- Consider emotional and practical needs
- Design with, not for, users
2. Collaborative
- Cross-functional team involvement
- Diverse perspective integration
- Co-creation with users
- Open sharing of ideas
3. Iterative
- Rapid prototyping and testing
- Continuous improvement
- Learning through failure
- Building on feedback
4. Action-Oriented
- Learning by doing
- Quick experimentation
- Tangible outputs
- Real-world testing
Best Practices
1. Start with Why
- Clearly define project goals
- Understand stakeholder needs
- Identify success criteria
- Align team objectives
2. Embrace Ambiguity
- Stay open to possibilities
- Avoid premature solutions
- Trust the process
- Welcome unexpected insights
3. Make It Tangible
- Create visual representations
- Build physical prototypes
- Show don’t tell
- Enable hands-on interaction
4. Fail Forward
- Learn from mistakes
- Test early and often
- Gather actionable feedback
- Iterate based on learning
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Time Constraints
Solution:
- Focus on quick iterations
- Use time-boxed activities
- Prioritize key insights
- Start small and scale
2. Stakeholder Buy-In
Solution:
- Show, don’t tell
- Demonstrate early wins
- Involve stakeholders early
- Share user insights
3. Team Alignment
Solution:
- Regular sharing sessions
- Clear documentation
- Visual communication
- Shared success metrics
Implementation Tips
- Start Small
- Begin with pilot projects
- Focus on quick wins
- Build momentum gradually
- Document learning
- Build Capability
- Train core team members
- Practice key methods
- Share knowledge
- Create resources
- Create Space
- Dedicate time for activities
- Set up physical space
- Provide needed materials
- Enable collaboration
- Measure Impact
- Define success metrics
- Track progress
- Gather feedback
- Share outcomes
Conclusion
Design Thinking provides a structured yet flexible approach to innovation and problem-solving. Its emphasis on human needs, iterative development, and collaborative problem-solving makes it particularly valuable for complex challenges. While the process may seem simple, its power lies in the mindset it creates and the framework it provides for turning insights into action.
Success with Design Thinking comes from practice, patience, and a willingness to learn from failure. Organizations that embrace these principles often find they not only solve immediate challenges more effectively but also build lasting capability for innovation and user-centered design.